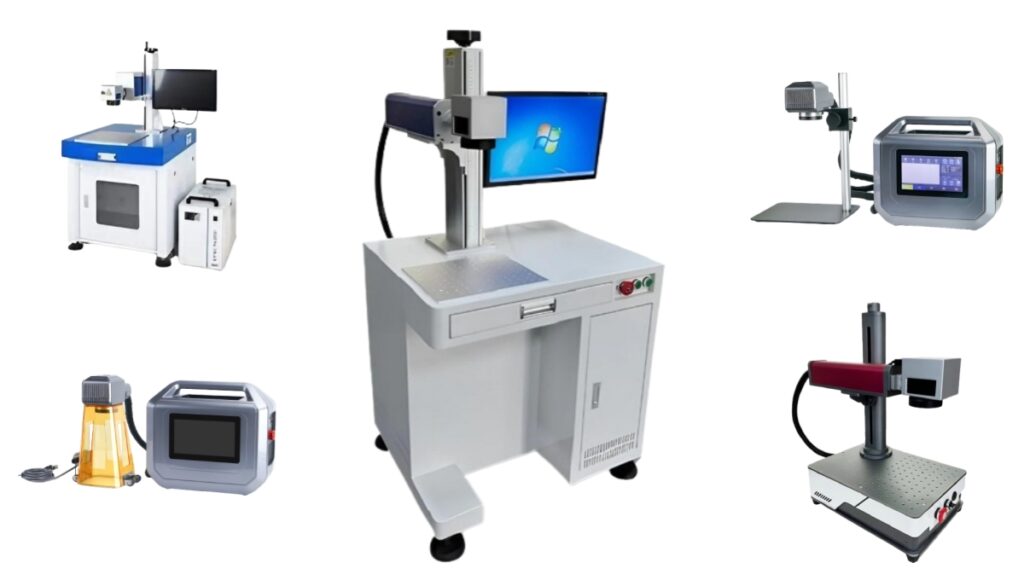

Laser marking machines have revolutionized the manufacturing world, offering precision, speed, and versatility across multiple industries. These devices utilize laser beams to engrave, etch, or mark various materials with high accuracy. Whether you’re marking serial numbers, logos, barcodes, or intricate designs, laser marking has become an essential part of product identification and traceability. But what exactly does a laser marking machine do, and why is it so vital in today’s world of industrial manufacturing?
In this article, we will explore how laser marking machines work, their applications, and the unique benefits they offer to different industries.
1. How Does a Laser Marking Machine Work?
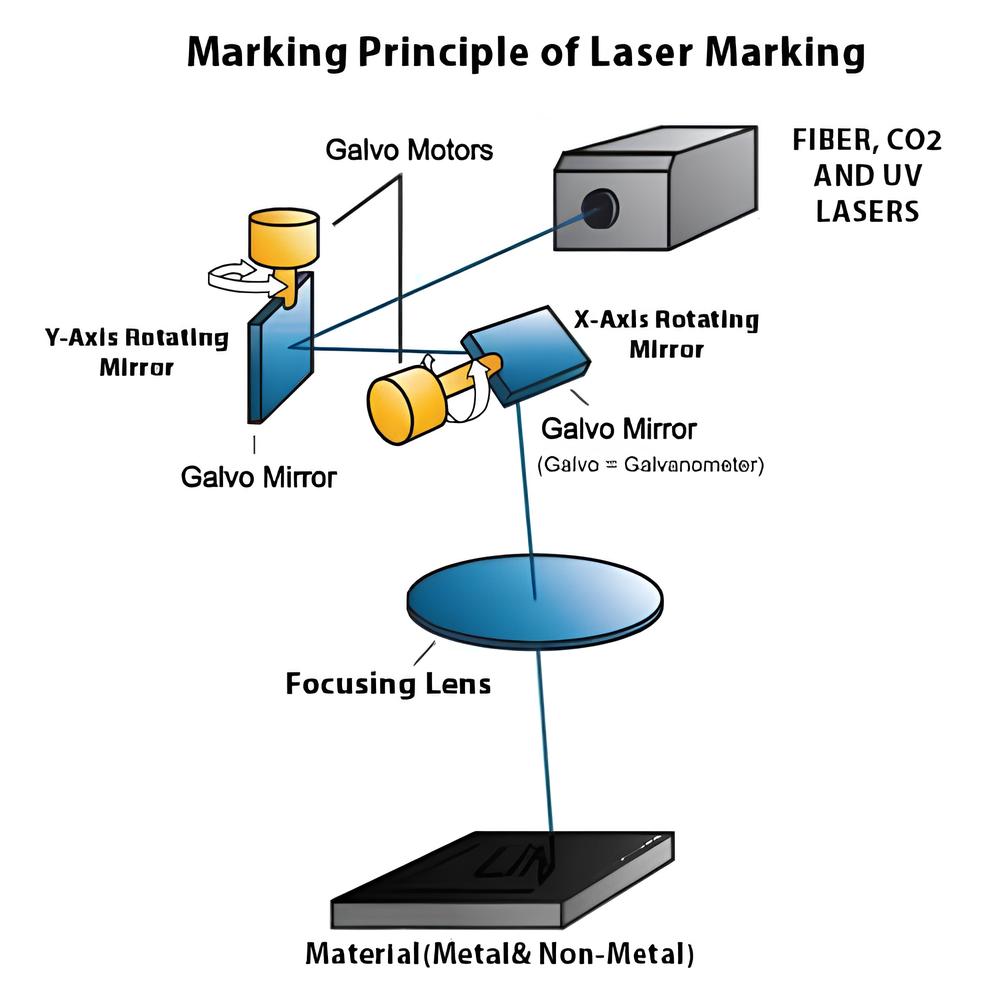
A laser marking machine uses a concentrated laser beam to make permanent markings on the surface of various materials. The machine focuses the laser beam onto a small area of the material, altering its surface properties. The beam creates high-energy pulses that interact with the material, resulting in visible marks like text, graphics, or codes.
The key advantage of this technology is precision—laser marking provides clean, accurate results without physically touching the material, reducing wear and tear on tools and the marked object itself. It also allows for a high degree of customization, enabling intricate designs on tiny surfaces, like circuit boards or medical devices.
2. Applications of Laser Marking Machines
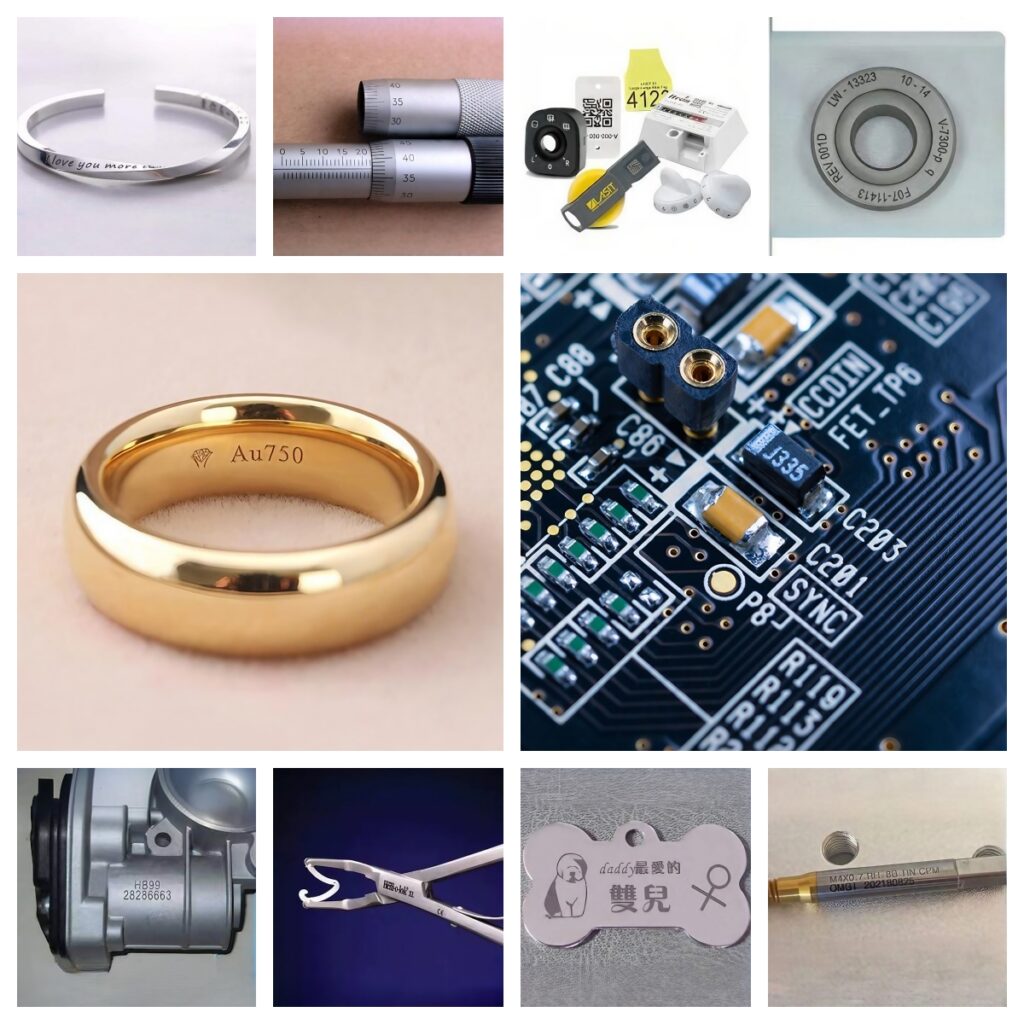

Laser marking machines have found widespread applications in various industries. These include:
- Electronics and Semiconductors: Laser marking is often used to engrave identification codes, logos, and serial numbers on electronic devices, circuit boards, and semiconductors.
- Automotive Industry: In the automotive sector, laser marking is used for engine components, part identification, and VIN markings.
- Medical Devices: Due to the precision required, laser marking is the preferred method for marking medical devices, where detailed labels or instructions must be permanently etched without damaging the device.
- Packaging: Packaging for consumer goods often utilizes laser marking for barcodes, batch numbers, and expiration dates.
- Jewelry and Watches: Intricate designs and logos can be engraved on jewelry and luxury watches with extreme precision.
- Aerospace: Laser marking is also critical in the aerospace sector, where parts must be traceable and tamper-proof.
3. Different Types of Laser Marking

There are four main types of laser marking, each offering unique benefits depending on the material and application.
- Engraving: The laser beam physically removes material to create deep, permanent engravings. This method is used when durability is crucial, such as in metal components or heavy-duty industrial parts.
- Etching: Laser etching involves creating shallow marks on the surface of a material, often used for barcodes or serial numbers on metals or plastics.
- Annealing: This process is used for marking metals, especially stainless steel, and involves heating the surface to change its color without affecting the material’s integrity.
- Foaming: Primarily used on plastics, foaming creates raised markings by melting the surface, which then bubbles and solidifies, forming a contrasting color.
4. Key Benefits of Laser Marking

Laser marking offers several advantages over traditional methods such as inkjet printing or mechanical engraving. These benefits include:
- Permanent Marks: Once applied, laser marks are extremely durable, resistant to wear, chemicals, and even heat.
- Non-Contact Process: The laser never touches the material, reducing the risk of damage or wear and enabling marking on delicate or intricate parts.
- High Precision: With its focused beam, laser marking can achieve extremely precise and fine details, making it suitable for electronics and medical applications.
- Environmentally Friendly: Laser marking produces no chemicals or waste, making it a greener alternative to traditional marking methods like ink-based printing.
5. Why Choose Laser Marking Over Traditional Methods?

Compared to traditional marking methods like mechanical engraving, inkjet printing, or stamping, laser marking offers distinct advantages:
- Durability: While inkjet printing may fade over time, laser markings are permanent and do not degrade, ensuring long-lasting identification.
- Low Maintenance: Mechanical engravers wear out and require replacement, while laser marking machines have minimal maintenance costs due to the lack of physical contact.
- Speed and Efficiency: Laser marking is faster and more efficient than many traditional methods, improving throughput in high-volume production lines.
6. Best Materials for Laser Marking

Laser marking works on a wide variety of materials, making it highly versatile for different industries. Common materials include:
- Metals: Stainless steel, aluminum, copper, brass
- Plastics: ABS, polycarbonate, polypropylene
- Wood: Commonly used in furniture and decorative items
- Ceramics: Used for medical devices and aerospace parts
- Glass: Suitable for creating high-quality marks on glass surfaces
7. Conclusion: The Future of Laser Marking

In conclusion, laser marking machines are an essential tool for modern industries, offering a perfect blend of precision, durability, and flexibility. They are the go-to solution for marking critical information like serial numbers, barcodes, and logos on products without compromising the material’s integrity.
As industries continue to demand higher standards for product identification, laser marking technology will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in ensuring compliance, traceability, and brand recognition across multiple sectors.
